RambergOsgoodSteel
This command is used to construct a Ramberg-Osgood steel material object.
Model.uniaxial(“RambergOsgoodSteel”, name, E, fy, a, n)
| E |
float
|
Young’s modulus of elasticity |
| fy |
float
|
Yield stress. |
| a |
float
|
yield offset parameter |
| n |
float
|
Parameter to control the transition from elastic to plastic branches. Additionally controls the hardening of the material: by increasing \(n\), hardening ratio will be decreased. |
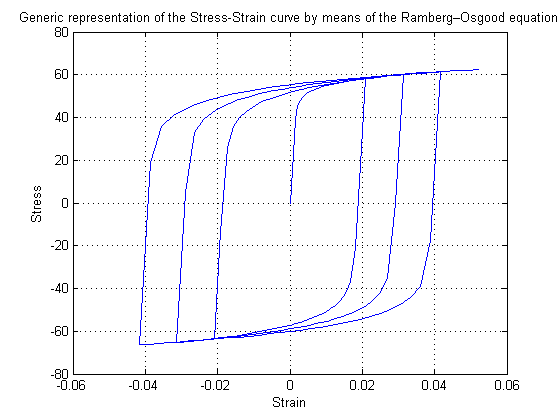
Introduction to the Ramberg-Osgood Material Model:
In earthquake engineering, Ramberg-Osgood functions are often used to model the behavior of structural steel materials and components. These functions are obtained when the power is normalized to an arbitrary strain, \(\varepsilon_0\), for which the plastic component of the strain, \(\varepsilon_\text{plastic}\), is not zero. Generally the yield strain, \(\varepsilon_y\), provides a good choice for normalization of strain.
The Ramberg-Osgood function is expressed as [1]:
\[ \varepsilon=\frac{\sigma}{E_{0}}+a \left(\frac{\sigma}{\sigma_{0}}\right)^{n} \]
Where E0 is the initial elastic modulus and σ0 is equal to Eε0.
More explanation about parameter “a” (yielding offset)
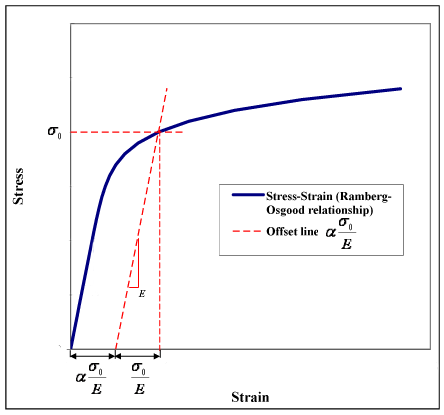
The value “a” which is equal to \(\alpha\frac{\sigma}{E_0}\) can be seen as a yield offset, as shown in Fig.1. This comes from the fact that
\[ \epsilon=\dfrac{(1+\alpha) \sigma_{0}}{E} \]
when σ=σ0.
Accordingly (see Fig.1):
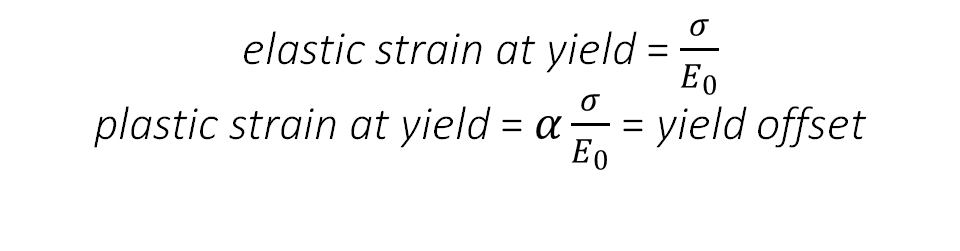
Values for α can also be found by means of fitting to experimental data, although for some materials, it can be fixed in order to have the yield offset equal to the accepted value of strain of 0.2%, which means [2]: \(\alpha \frac{\sigma}{E_{0}}=0.002\) .
References
Michel Bruneau, Chia-Ming Uang Andrew Whittaker. “Ductile Design of Steel Structures” McGraw-Hill Professional, 1997, ISBN: 0070085803 - 978-0070085800
Ramberg, W., & Osgood, W. R. (1943). “Description of stress-strain curves by three parameters.” Technical Note No. 902, National Advisory Committee For Aeronautics, Washington DC.
Contact Authors:
Reza Rahimi, Graduate Research Assistant of Structural Engineering, Dalhousie University, reza.rahimi@dal.ca
Reza Sepasdar, Graduate Research Assistant of Structural Engineering, Dalhousie University, reza.sepasdar@dal.ca
Mohammad Reza Banan, Associate Professor of Civil Engineering, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran, banan@shirazu.ac.ir